Life Lessons to Learn from Horse Riding
- A Sense of Confidence
- Trust Building
- Overcome all fears
- Affection
- Positive approach
- Learn something new & Making newer mistakes
- Sense of achievement
- Build the personality
- Improve learning ability
- Get better at problem-solving, and
- Sharpen focus
International Baccalaureate® (IB) curriculum physical and health education empowers students to understand and appreciate the value of being physically active and to develop the motivation for making healthy life choices.
We are making lesson and unit plans in alignment with IB curriculum, help documenting progress for below objectives.
Objectives of program are
Build positive relationships, Boosting their abilities in collaboration, communication as well as their understanding of social responsibility Competencies and skills that bolster their attainment
Students are challenged to develop their understanding through units that require performance planning, the application of theoretical and practical knowledge and post-performance reflection and evaluation
The IB Primary Years Programme (PYP) for children aged 3 – 12 nurtures and develops young students as caring, active participants in a lifelong journey of learning.
The PYP offers an inquiry-based, transdisciplinary curriculum framework that builds conceptual understanding. It is a student-centered approach to education for children aged 3-12. It reflects the best of educational research, thought leadership and experience derived from IB World Schools.
The PYP has evolved to become a world leader in future-focused education. The PYP is an example of best educational practice globally, responding to the challenges and opportunities facing young students in our rapidly changing world.
The PYP curriculum framework
The PYP curriculum framework begins with the premise that students are agents of their own learning and partners in the learning process. It prioritizes people and their relationships to build a strong learning community.
PYP students use their initiative to take responsibility and ownership of their learning. By learning through inquiry and reflecting on their own learning, PYP students develop knowledge, conceptual understandings, skills and the attributes of the IB Learner profile to make a difference in their own lives, their communities, and beyond.
The framework emphasizes the central principle of agency, which underpins the three pillars of school life:
Embedded in the framework is the recognition of the importance of fostering an individual’s self-efficacy. Students with a strong sense of self-efficacy are active in their own learning and take action in their learning community.
Why offer the PYP?
The PYP focuses on the development of the whole child as an inquirer, both in school and in the world beyond. The PYP offers a transformative experience for students, teachers and whole school communities and delivers excellent outcomes by providing an education that is engaging, relevant, challenging and significant.
PYP learners know how to take ownership of their learning, collaborating with teachers to deepen understanding and increase their confidence and self-motivation. Through actively engaging in integrated ongoing assessment they become effective, self-regulated learners who can act on constructive feedback.
Guided by six transdisciplinary themes of global significance, students broaden their learning by developing their conceptual understandings, strengthening their knowledge and skills across, between and beyond subject areas.
What is PSPE in PYP?
Personal, Social and Physical Education (PSPE)
IB mission statement
The International Baccalaureate aims to develop inquiring, knowledgeable and caring young people who help to
create a better and more peaceful world through intercultural understanding and respect.
To this end the organization works with schools, governments and international organizations to develop
challenging programmes of international education and rigorous assessment.
These programmes encourage students across the world to become active, compassionate and lifelong learners
who understand that other people, with their differences, can also be right.
IB learner profile
The aim of all IB programmes is to develop internationally minded people who, recognizing their common humanity and shared guardianship of the planet, help to create a better and more peaceful world.
IB learners strive to be:
Inquirers They develop their natural curiosity. They acquire the skills necessary to conduct inquiry and research and show independence in learning. They actively enjoy learning and this
love of learning will be sustained throughout their lives.
Knowledgeable They explore concepts, ideas and issues that have local and global significance. In so doing, they acquire in-depth knowledge and develop understanding across a broad and
balanced range of disciplines.
Thinkers They exercise initiative in applying thinking skills critically and creatively to recognize
and approach complex problems, and make reasoned, ethical decisions.
Communicators They understand and express ideas and information confidently and creatively in more than one language and in a variety of modes of communication. They work effectively
and willingly in collaboration with others.
Principled They act with integrity and honesty, with a strong sense of fairness, justice and respect for the dignity of the individual, groups and communities. They take responsibility for
their own actions and the consequences that accompany them.
Open-minded They understand and appreciate their own cultures and personal histories, and are open to the perspectives, values and traditions of other individuals and communities. They are accustomed to seeking and evaluating a range of points of view, and are willing to grow
from the experience.
Caring They show empathy, compassion and respect towards the needs and feelings of others.
They have a personal commitment to service, and act to make a positive difference to the
lives of others and to the environment.
Risk-takers They approach unfamiliar situations and uncertainty with courage and forethought,
and have the independence of spirit to explore new roles, ideas and strategies. They are
brave and articulate in defending their beliefs.
Balanced They understand the importance of intellectual, physical and emotional balance to
achieve personal well-being for themselves and others.
Reflective They give thoughtful consideration to their own learning and experience. They are able to assess and understand their strengths and limitations in order to support their learning and personal development.
Identity An understanding of our own beliefs, values, attitudes, experiences and feelings and how they shape us; the impact of cultural influences; the recognition of strengths, limitations and challenges as well as the ability to cope successfully with situations of change and adversity; how the learner’s concept of self and feelings of self-worth affect his or her approach to learning and how he or she interacts with others.
Active living An understanding of the factors that contribute to developing and maintaining a balanced, healthy lifestyle; the importance of regular physical activity; the body’s response to exercise; the importance of developing basic motor skills; understanding and developing the body’s potential for movement and expression; the importance of nutrition; understanding the causes and possible prevention of ill health; the promotion of safety; rights and the responsibilities we have to ourselves and others to promote well-being; making informed choices and evaluating consequences, and taking action for healthy living now and in the future.
Interactions An understanding of how an individual interacts with other people, other living things and the wider world; behaviors, rights and responsibilities of individuals in their relationships with others, communities, society and the world around them; the awareness and understanding of similarities and differences; an appreciation of the environment and an understanding of, and commitment to, humankind’s responsibility as custodians of the Earth for future generations.
The PSPE strands Well-being of the learner
Interactions
Active living
Identity
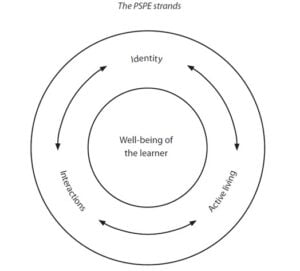
Developing well-being through PSPE
Each learner is a unique individual with different life experiences and no two learning pathways are the same. Learners within the same age group will have different needs and demonstrate different performance levels; therefore, teachers should consider a range of phases when planning learning experiences for a class.
Learners are likely to display understanding and skills from more than one of the phases at a time. The continuums are not prescriptive tools that assume a learner must attain all the outcomes of a particular phase before moving on to the next phase, nor that the learner should be in the same phase for each strand.
It is important to note that all three of the strands interact with each other and have relevance across and throughout the curriculum. It is therefore likely that teachers will refer to all three continuums to inform planning, teaching and assessing.
A balanced curriculum would include the following types of experiences.
- Individual pursuits: The development of basic motor skills and the body’s capacity for movement through locomotor and manipulative skills and/or experiences; the techniques, rules and purpose of a range of athletic activities (for example, track and field, swimming, skating, skiing); recognizing a high level of achievement and how to improve a performance.
- Movement composition: Recognizing that movements can be linked together and refined to create a sequence of aesthetic movements. Movements can be in response to stimuli or performance elements and/or criteria and can communicate feelings, emotions and ideas (for example, gymnastics, dance*, martial arts).
- Games: Recognizing the challenges presented by games; the importance of manipulating space; the categorizing of games; identifying and developing appropriate skills and strategies; recognizing the importance of rules and how they define the nature of a game; modifying existing games and creating new games; teamwork.
- Adventure challenges: A variety of tasks requiring the use of physical and critical-thinking skills by individuals and/or groups; challenges that require groups to work together collaboratively in order to solve problems and accomplish a common goal; recognizing the role of the individual in group problem solving.
- Health-related fitness: Recognizing and appreciating the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle; the body’s response to exercise including the interaction of body systems and the development of physical fitness.
On The Lines, Off The Lines | Physical Education Game (Fundamental Movement Skills) – YouTube
Frogs & Fish – Physical Education Game (Fundamental Movement Skills)
Course Features
- Lectures 9
- Quizzes 0
- Duration 48 weeks
- Skill level All levels
- Language English
- Students 1000
- Certificate No
- Assessments Yes





